OKAMURA Masashi Professor
My DreamGlobal food safety and stable food supply based on control of infectious diseases in animals
ThemeElucidating host-specific pathogenesis and understanding pathogen-host co-evolution for control of infectious diseases
Field
Keyword
Instructable research topic for doctoral thesis
- 家禽チフス・ひな白痢の病原メカニズムの解明
- 牛サルモネラ症の疫学調査と制御法の確立
- 馬パラチフスの病原メカニズムの解明
Message
私は、いわゆる「町の獣医さん」を目指して獣医大学に入学しましたが、入学後に獣医師の職域の広さに驚かされました。私はその後これまで様々な人との出会いや導きによって、当初の目標であった臨床獣医師ではなく、病原細菌や動物の感染症に関する研究・教育に携わる大学教員として現在に至っています。
人生は選択の連続です。しかし、「人生大博打」ではなく、様々な経験を通して自ら得た一次情報に基づいて、その選択肢を自分で絞り込み、選択し、その人生を納得して過ごすことが重要であり、それが充実感や幸福につながります。時には引き返したりやり直したりすることもあるでしょう。そんな時のためにも、学生の間にしかできない様々な学外実習には積極的に参加し、自分の様々な可能性や将来像をイメージしながら6年間を有意義に過ごしてください。
国家試験までは、知識を蓄積し、解答のある問題を解くことが中心ですが、獣医師になってからはどの職業を選んでも「自分で問題を見つけて自分なりの答えを導き出す」ことが必要になります。知識も知恵も必要ですが、それに基づいて自分で考えることがより重要です。このリサーチマインドを養うためにも、私とともに研究を楽しみませんか?
| Academic degree | Ph.D.in Veterinary Sciences |
| License | Veterinarian |
| Self introduction |
I was born in Osaka , but have spent more than half of my life in Aomori and Hokkaido. |
| Room address | General Research Building 1 |
| Room number | S2102-1 |
| Mail address | okamuram  obihiro.ac.jp
obihiro.ac.jp |
Belongs
Research Department/Department of Veterinary Medicine/Division of Veterinary Sciences/Section of Applied Veterinary SciencesOffice for International Accreditation of Veterinary Education/StaffDiagnostic Center for Animal Health and Food Safety/Bacteriology LaboratoryIntroduction
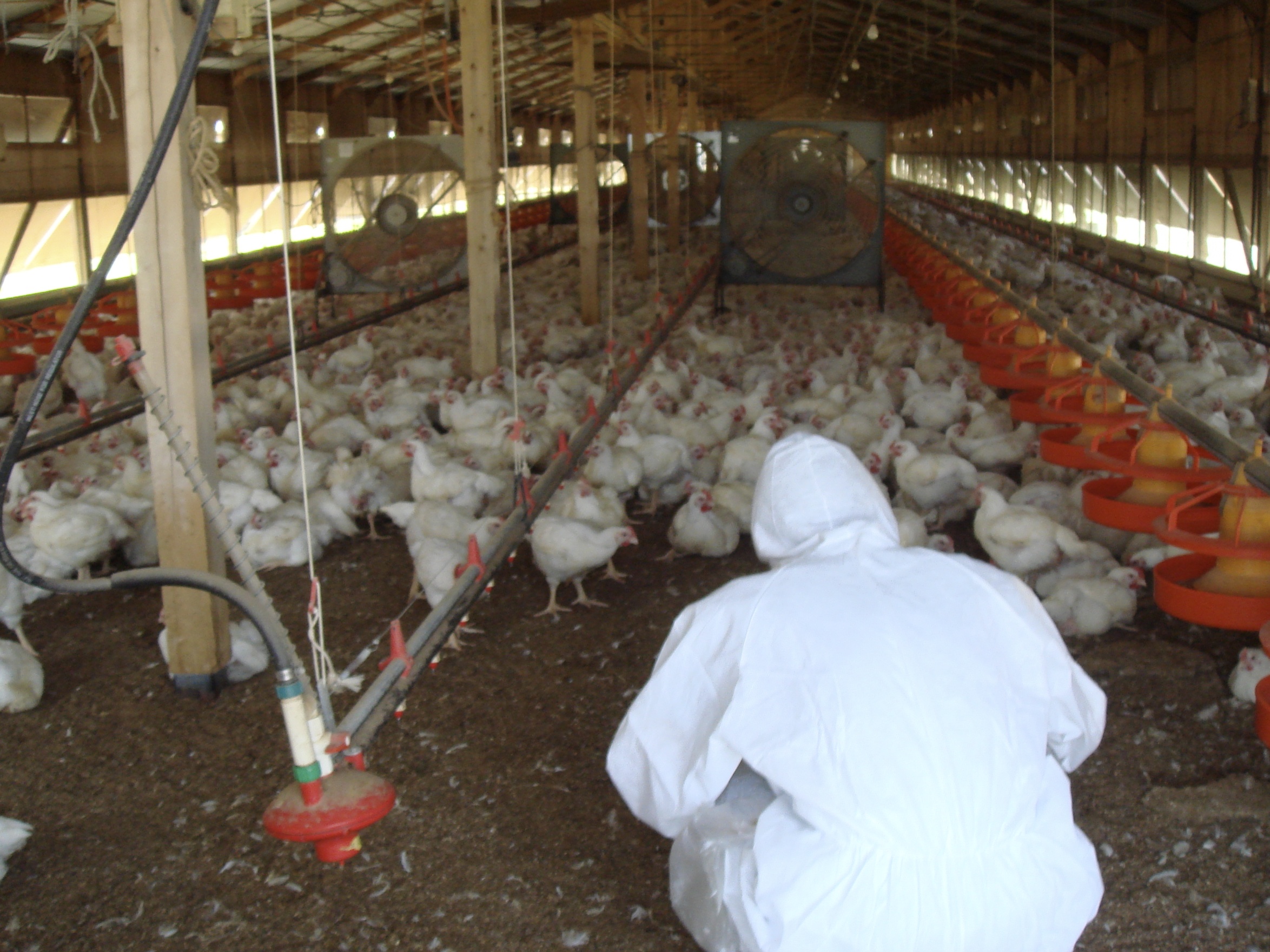
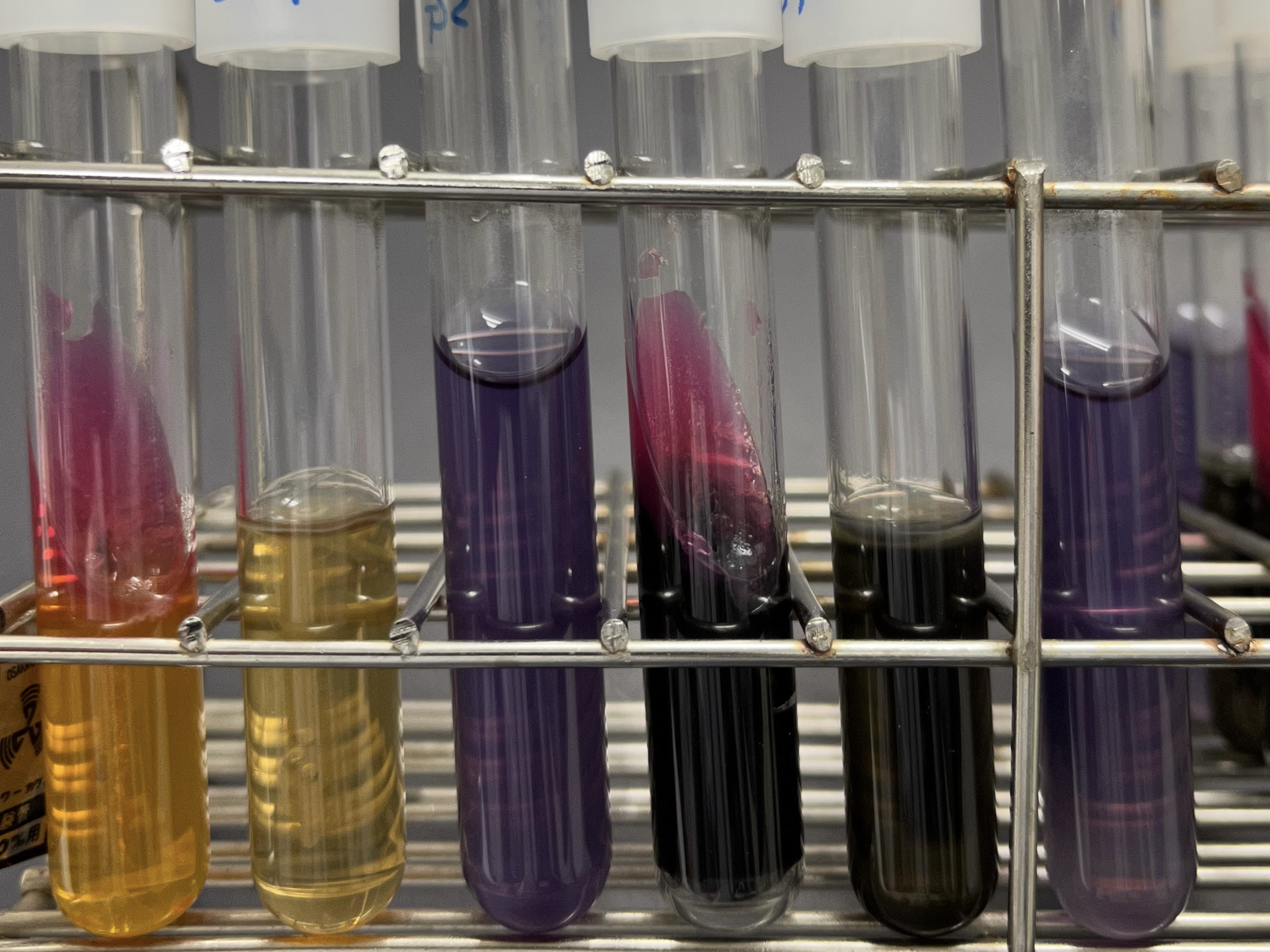
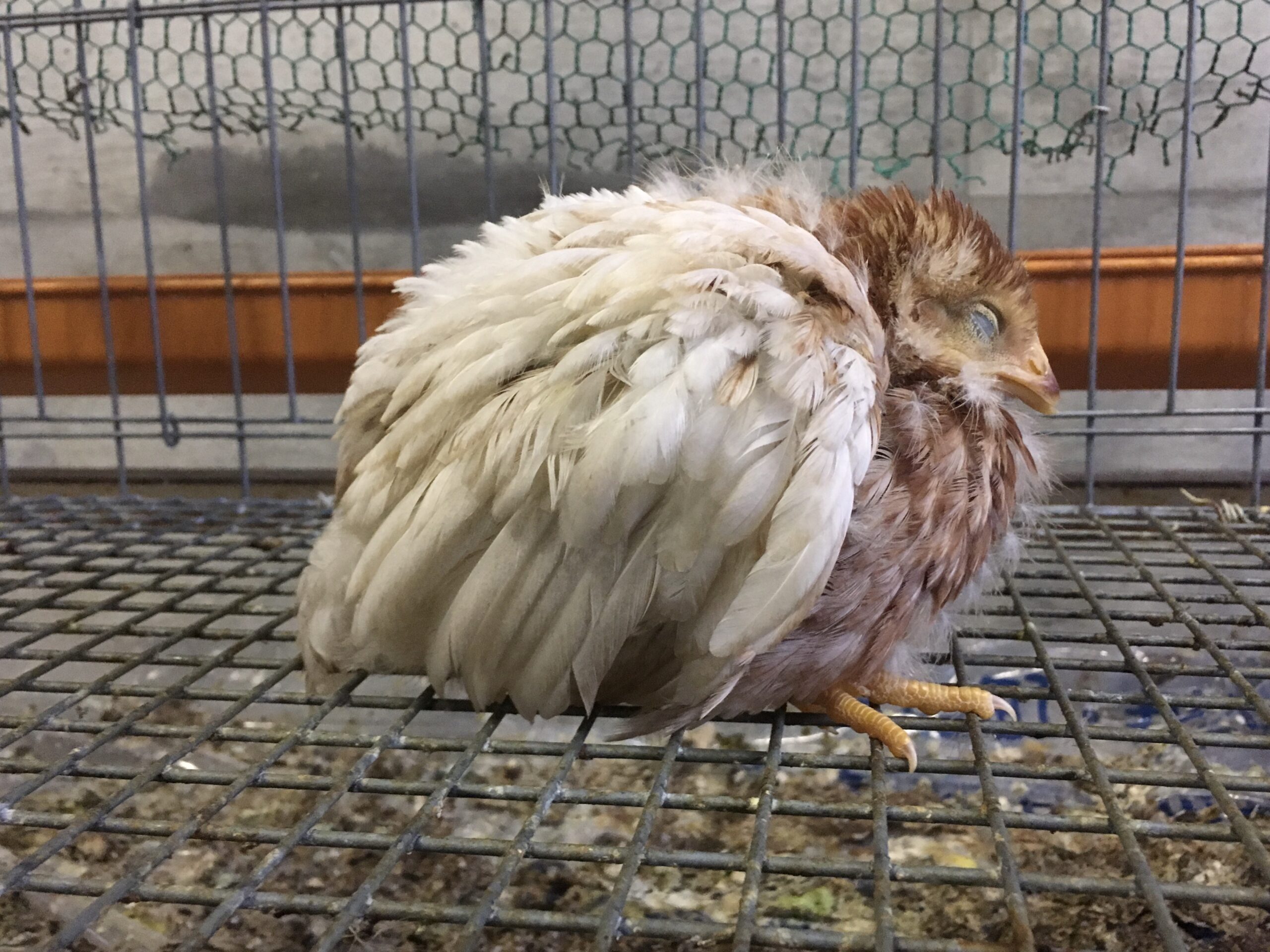
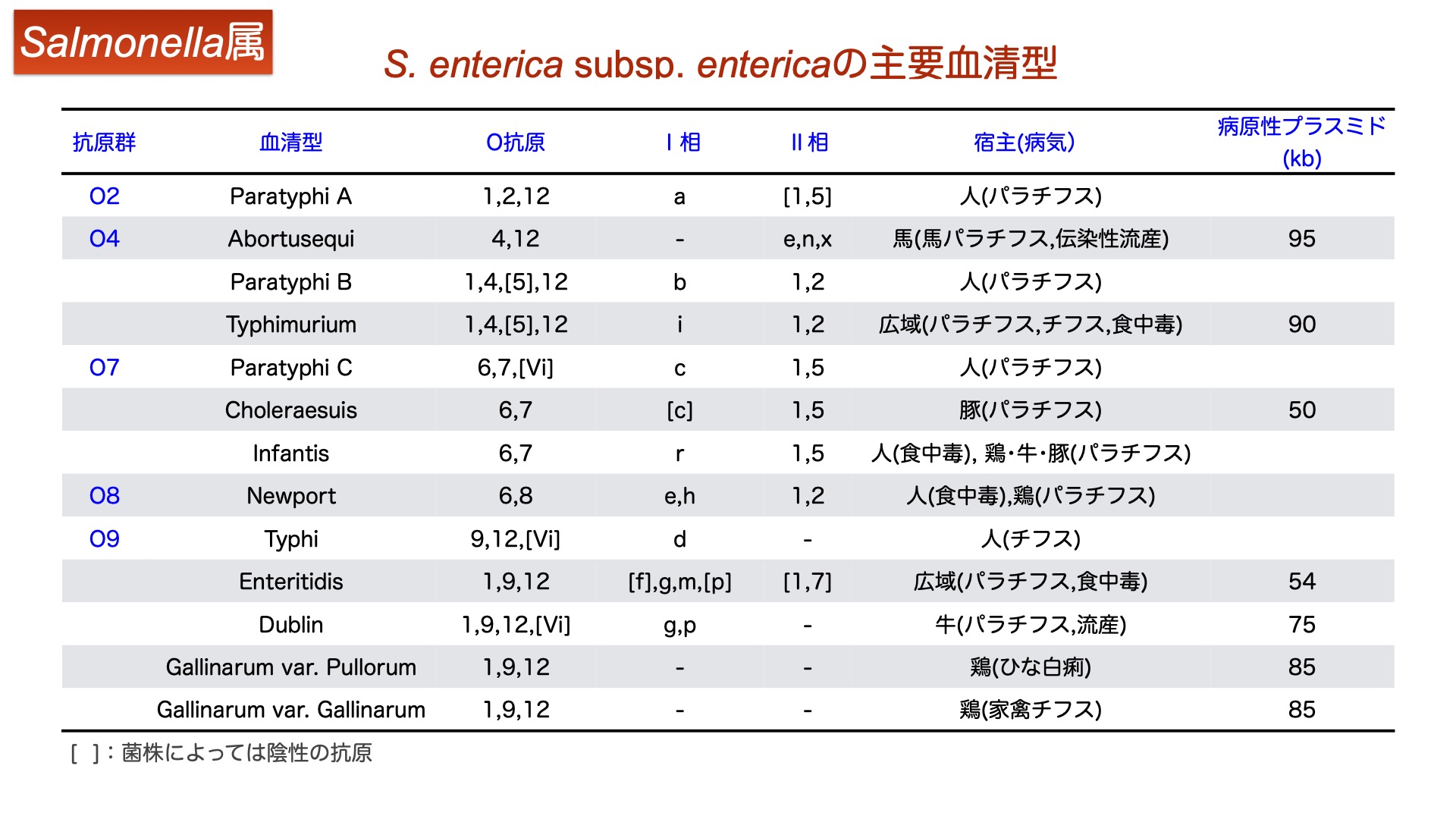
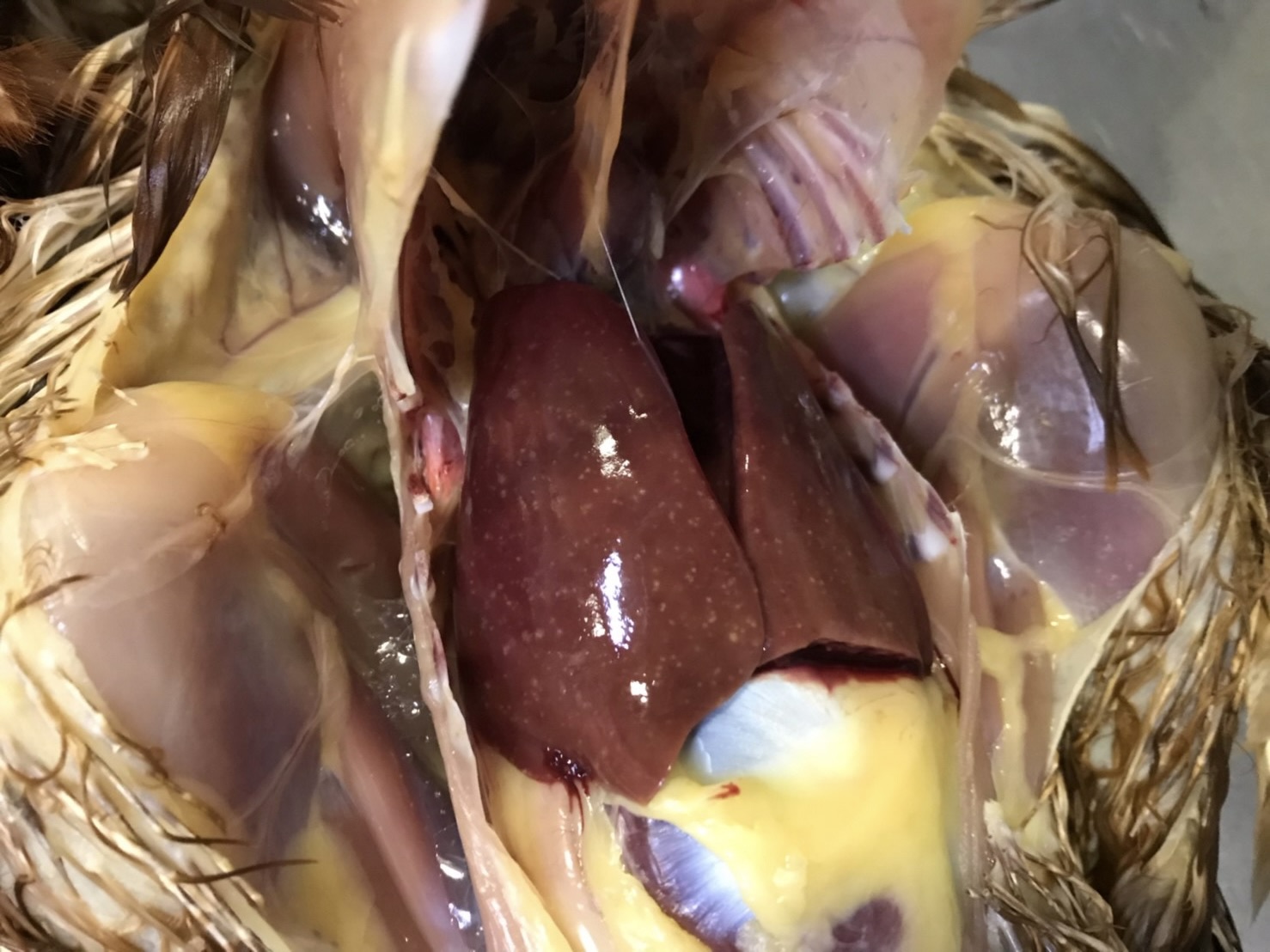
Salmonella are classified into as many as 2,700 serovars according to the combination their somatic and flagellar antigens. Many of the pathogenic serovars cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms in a variety of animals (food poisoning in humans). On the other hand, only a few serotypes (less than 10) cause septicemia in specific animals, leading to death. However, the mechanism that causes this strong host-specific virulence has not yet been elucidated. We have identified 50 antigens that are expressed by serovar Gallinarum (fowl typhoid) in infected chickens. We have also used mutant strains lacking the genes encoding these antigens to elucidate how these genes are involved in the pathogenesis of fowl typhoid, and been attempting to identify the genes essential for host-specific virulence and lethality and the mechanisms involved, compared with those of serovar Typhimurium, which has been commonly used in studies of Salmonella. We are also currently working on serovars Dublin and Abortusequi, which infects cattle and horses, respectively, and hope to eventually update our overall understanding of the pathogenicity of Salmonella spp.
Through this research, we hope to unravel the history of the co-evolution of pathogenic bacteria and their host animals, and furthermore, to elucidate how zoonotic pathogens have become able to infect various animal species, thereby contributing to the development of control measures for human and animal infectious diseases.


List of current research topics
- Elucidation of pathogenic mechanisms of fowl typhoid/pullorum disease
- Epidemiological investigation of bovine salmonellosis and establishment of control strategies
- Elucidation of pathogenic mechanisms of equine paratyphoid
| Related industries | Poultry/livestock industry, Animal Health, Pharmaceutical products (vaccines etc.) for animals, Food Safety |
| Affiliated academic society | The Japanese Society of Veterinary Science, The Japanese Society on Poultry Diseases, Japanese Society for Bacteriology, Japan Society of Veterinary Epidemiology, Japanese Society of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, Japanese Society of Food Microbiology |
| Editorial Board |
|
| Academic background | 1992-1998: BVSc in Kitasato University School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Sciences 1998-2002: Ph.D. in Osaka Prefecture University Graduate School of Agriculture and Biological Sciences Mar 2001-Mar 2002: Visiting Scientist in USDA-ARS (Beltville, MD, USA) Apr 2002-Nov 2002: Postdoc Scientist in USDA-ARS (Beltville, MD, USA) Dec 2002-Dec 2004: Postdoc in National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases, Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinar Medicine Jan 2005-Dec 2020: Research Associate - Associate Professor in Kitasato University School of Veterinary Medicine Jan 2021-Present: Professor in Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinar Medicine |






