KUBOTA Akira Professor
My DreamContribute to improving animal, food, and environmental hygiene from the viewpoint of toxicology
ThemeResearch on hazard assessment and toxic mechanism of anthropogenic and natural compounds that threat food safety as well as human and animal health, and on species-specific drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics aiming at advanced veterinary medicine for rare animals
Field
Keyword
Instructable research topic for doctoral thesis
- 小型魚類をモデルとした化学物質の有害性評価と毒性発現機構に関する研究
- 希少動物の薬物感受性評価法の確立と投薬応用に関する研究
- 化学物質感受性の種差に関する比較毒性学的研究
- シトクロムP450の生理学的・毒性学的役割および発現制御機構の解明
Message
本学の学生さんには,自然界・生命の現象に幅広い見識を持つということと,興味を持ったテーマを集中的に掘り下げること,この両面にバランスよく柔軟に向き合うことで,確固とした哲学を持ちつつ物事を俯瞰する能力を養ってほしいと思います。こうした努力を続けることで,毒性学に限らず様々な分野において,学際性・専門性の高い研究に取り組むための素地をつくることができると思います。
毒性学研究室ではとくに研究職志望の学生さんを歓迎します。生命科学的アプローチによる毒性学研究に興味を持った方であればユニットは問いません。「こういう研究がやりたいけどできるか」とか「研究者として将来海外で研鑽を積みたいけど何から始めたらよいか」などありましたら気軽にお問い合わせください。
| Academic degree | D.Agr. |
| Self introduction |
Was born in Kanagawa Prefecture, and came to join here in March 2014. While I was an undergraduate, I learned environmental pollution caused by anthropogenic chemical substances like dioxins and their potential adverse effects on wildlife, which became my motivation to study biological defence system against xenobiotics. Since then, I am consistently studying "toxicology". |
| Room address | General Research Building iV |
| Mail address | akubota  obihiro.ac.jp
obihiro.ac.jp |
Belongs
Research Center for Global Agromedicine/Department of Veterinary MedicineResearch Department/Department of Veterinary Medicine/Division of Veterinary Sciences/Section of Physiology and PharmacologyDiagnostic Center for Animal Health and Food Safety/Toxicology Laboratory Office for International Accreditation of Veterinary Education/StaffIntroduction
Major research topics in our research group are as follows:
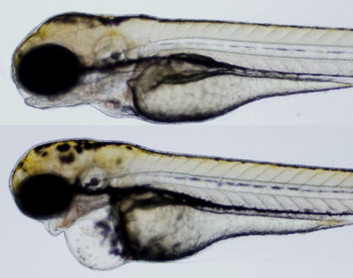
- Understanding adverse effects and toxic mechanisms of chemical substances using zebrafish as a model species
You may wonder why zebrafish is being used in a field of veterinary sciences at OUAVM. To date zebrafish have been extensively used as a vertebrate model species in a stunning array of research projects in embryology and medical science. In concurrence with daphnia and algae, zebrafish have been used also for assessing chemical effects on ecosystem. Benefit to using zebrafish as a model for those research subjects includes 1) high homology to human and other mammals at a genomic level, 2) having feature of high fecundity and rapid development with transparency, making it possible to observe organogenesis, 3) ease of genetic manipulation and inhibition of gene function, etc.
In case livestock animals are exposed heavily to chemical substances such as pesticides, antibiotics, mycotoxins, and environmental contaminants, decline of their productivity may be of great concern. High levels of exposure may also cause adverse human health effects via consumption of livestock products that are contaminated with those chemicals. Alternatively, exposure of wildlife to those chemicals may cause detrimental effects on ecosystem through the population decline. In our laboratory, we investigate hazard assessment and toxic mechanism of anthropogenic and natural compounds that potentially threat food safety as well as human and animal health, aiming at contribution to improving animal, food, and environmental hygiene. - Development of assessment method for drug sensitivity in endangered species, aiming at clinical application
In veterinary medicine of wild animals including endangered ones, there often is difficulty in choice of drugs and dosage regimen, due largely to species difference in susceptibility and response to drugs. A key strategy to address these issues is to establish an effective dosage regimen based upon species-specific pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD). However, it is difficult to evaluate drug sensitivity and PK/PD as basic information in endangered species because of challenges for conducting administration test with live animals as well as limited availability of fresh tissue samples to work on drug-metabolizing enzymes. Our approach to address these issues is, with the assistance of zoo, 1) to heterologously express (in yeast or bacteria) drug-metabolizing enzymes (e.g., cytochrome P450) that are predominant in liver of a particular species, 2) to examine potency of the expressed enzymes to metabolize drugs that are frequently used in clinical practice and inhibitory effects of drugs on the enzyme functions, and 3) to predict dosage and administration based upon data from those in vitro studies and establish the appropriate dosage regimen through the clinical application with injured or diseased individuals.


List of current research topics
- Understanding adverse effects and toxic mechanisms of chemical substances using zebrafish as a model species
- Development of assessment method for drug sensitivity in endangered species aiming at clinical application
- Comparative toxicology toward understanding species difference in susceptibility to chemical substances
- Physiological and toxicological roles and regulation of cytochrome P450
- Surveillance of mycotoxins contamination in corn for animal consumption
| Related industries | Environmental Sciences, Drugs, Veterinary Sciences, Animal industry |
| Affiliated academic society | The Japanese Society of Toxicology, Society of Toxicology, Japan Socieity for Environmental Chemistry, Japan Society of Endocrine Disruptors Research, Japan Society of Comparative Pharmacology and Toxicology, Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme Research Group, The Japanese Society of Environmental Toxicology, The Japanese Society of Veterinary Science, Hokkaido Drug Action Reserach Group |
| Academic background | 2003-2006 Ehime University (JSPS DC1) 2006-2007 Ehime University (Postdoc) 2007-2009 Rakuno Gakuen University (JSPS PD) 2009-2014 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (JSPS Postdoctoral Fellowship for Research Abroad, etc.) 2014-present Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine |





